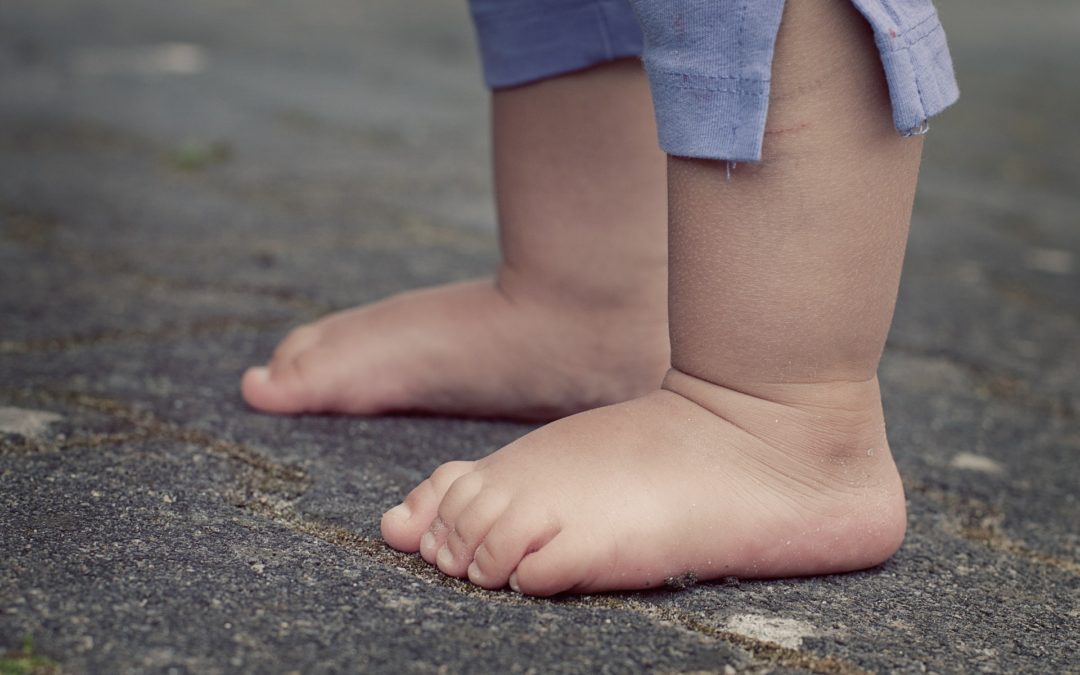
Children from the ages from infancy till toddler will present with a ‘flat foot’ which is completely normal as their joints are still mobile and their fat pad can cover up a developing arch (‘medial longitudinal arch’ – which is commonly viewed to determine flat foot).
A flat foot appears with the heel and Achilles rolled inwards with the visible side foot arch collapsed or rolled downwards excessively. As a result, this poor foot posture can lead to mild to severe symptoms such as muscle fatigue, impaired performance and joint pain.
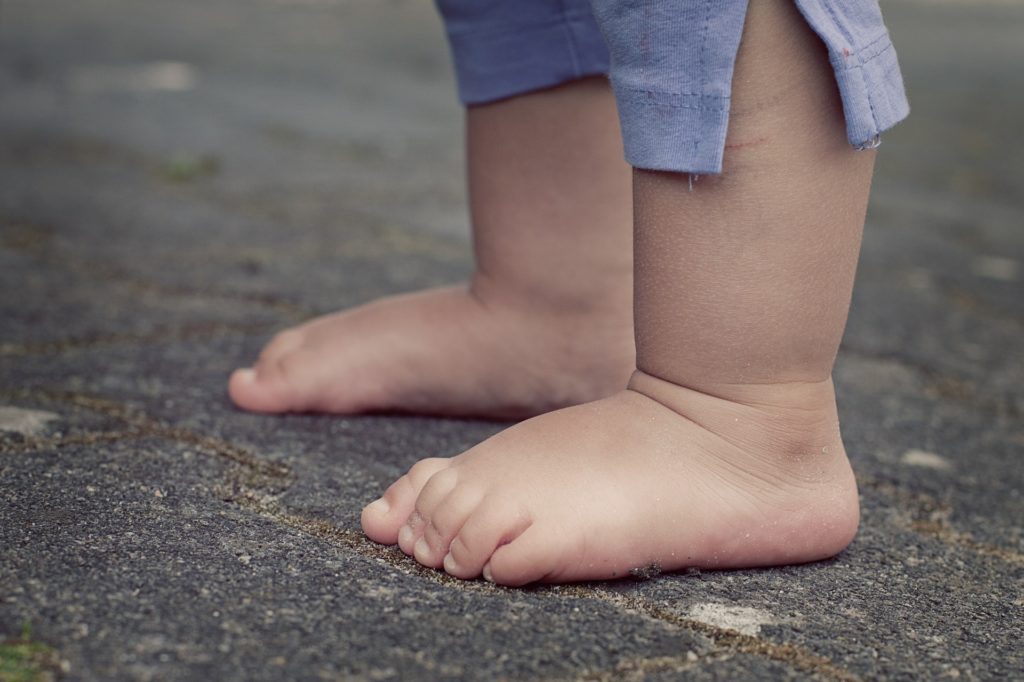

By the age of 5-6 years old, a child’s foot should’ve developed a medial longitudinal (ML) arch however, don’t panic a ML arch can still be strengthened and developed within 10 years of their early life. 1
TYPES
Paediatric flat feet can get very complex but to keep this article as a quick read, I’ll just keep it down to the 2 primary types – flexible and rigid.
Both flat feet types are aggravated by factors such as BMI, soft tissue laxity and lack of neuromuscular control.2
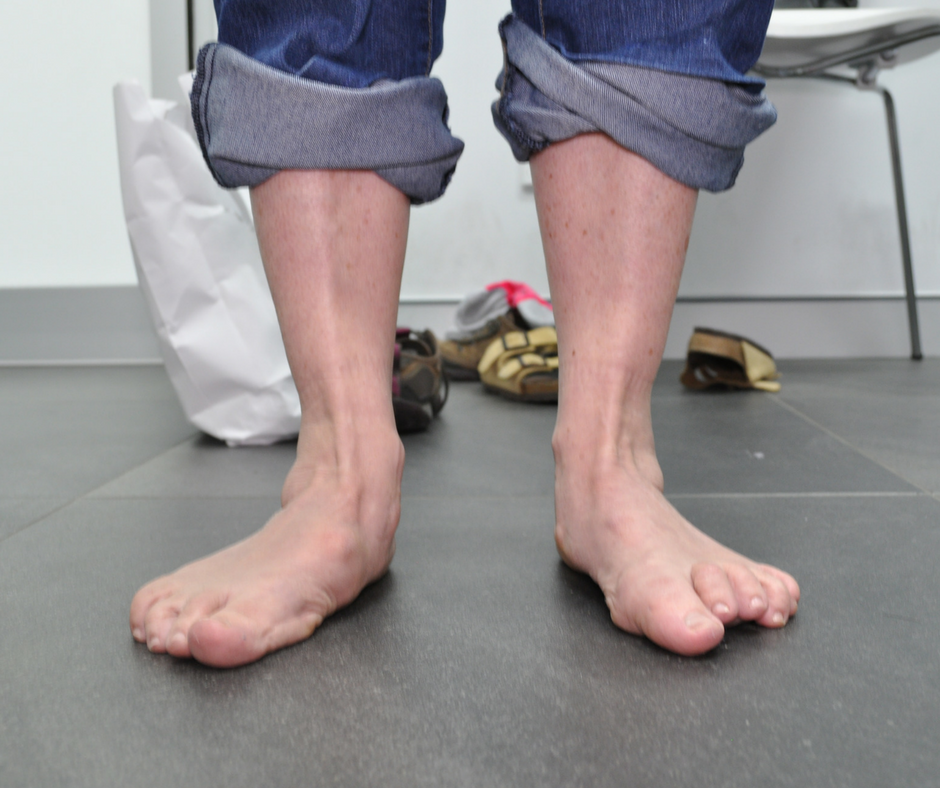
Flexible
Flexible paediatric flat foot is the most common flat foot type found in kids. It is defined as having an arch while not weight-bearing and having a flattened arch when weight-bearing. As a parent or caregiver, you may notice that your child’s feet are of this type but they may or may not complain of any symptoms.1
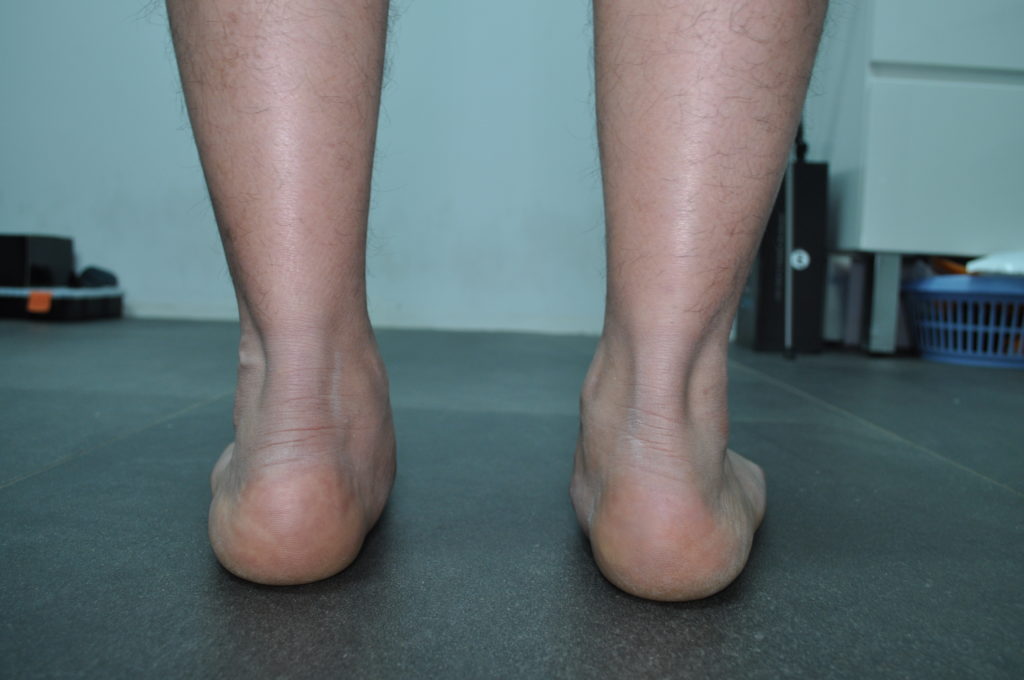
Rigid
Kids with a rigid flat foot type are not as common but the factors that caused this foot type may be down to underlying conditions. It is defined as having a flattened arch both when non-weight-bearing and weight-bearing. 2
SYMPTOMS
Flexible flat foot can appear with no symptoms, however if correct measures are not in place, it may lead to the following symptoms and their severity.
Common symptoms of paediatric flat feet include:
- Muscle fatigue
- Aches
- Heel pain
- Arch pain
- Knee pain
- Muscle cramping
- Paraesthesia
COMPENSATION
Most of the leading research has concluded that flat feet with no symptoms should be left untreated as there is nothing wrong with the feet. It is my opinion that I differ in my insight. Remember as I mentioned above that flat feet can be aggravated based on BMI/weight, soft tissue laxity and lack of neuromuscular control.
So what is compensation? To move, we utilise a set of muscles that fire to allow the movement however if our mechanics or our body, lower limb and foot posture is not in alignment then our body will have to recruit more muscles to produce that movement, thereby causing an increase in muscle fatigue, tightness and strain.
A simple example is if a child who walks ‘normally’ would say recruit 10 muscles however in a compensation state where they are dealing with flat foot they recruit 20 muscles may just to make that movement! When compensation occurs for kids with flat footed then that will certainly lead to pain and discomfort!
TREATMENT
At the initial stages of a diagnosed flexible flat foot then treatment would include activity modification, appropriate footwear and orthotics. The premise is to re-establish ‘foot core’ (http://triumphinstitute.com.au/video-strengthening-protecting-feet-injuries-establishing-strong-foot-core/) and redistribute pressure so that the child can perform at their highest physical potential with minimal compensation mechanisms.
Those children who suffer from rigid flat foot are most likely referred to an orthopaedic surgeon for surgical corrective opinion. But this really comes down to a thorough Podiatric postural assessment.
KEY POINTS
Kids with flat feet are extremely common as is more or less noticed by parents, teachers or caregivers. Please don’t be alarmed if your child appears to have a flat foot during the ages of infancy to 6 years old. It’s all part of their development however if poor movement, pain or discomfort is present then I highly recommend seeing a Podiatrist for their assessment and opinion.
WALK SMARTER NOT HARDER!

Grant Duong, Podiatry
At the Triumph Institute located in the heart of Bankstown, Sydney we also practice podiatry. It’s a medical field that specialises in the prevention, diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation of problems and issues that affect the lower limbs, from the lower back right down to our feet.
REFERENCES
[1] Halabchi, F., Mazaheri, R., Mirshahi, M. & Abbasian. L. (2013) Pediatric Flexible Flatfoot ; Clinical Aspects and Algorithmic Approach. Iran J Pediatr. 23(3) : 247-260
[2] Bauer, K., Mosca, V.S. & Zionts, L.E. (2016) What’s new in pediatric flat foot? J. Pediatr Orthop. 36(8): 865-869


